As residential users become increasingly conscious of their energy consumption, electricity costs, and grid reliability, home-based solar + storage systems are rapidly gaining popularity. For suppliers and technical trading professionals targeting small-scale energy projects, understanding the typical configurations for residential PV + ESS (Energy Storage System) setups is critical to offering meaningful advice and value-driven solutions.
This article explores the most common architectures of residential PV + storage systems, key components involved, and the technical criteria that determine which configuration is best suited for a given household or project. We’ll also address practical issues such as inverter selection, battery sizing, and daily load profiles.
1. What Is a Residential PV + Storage System?
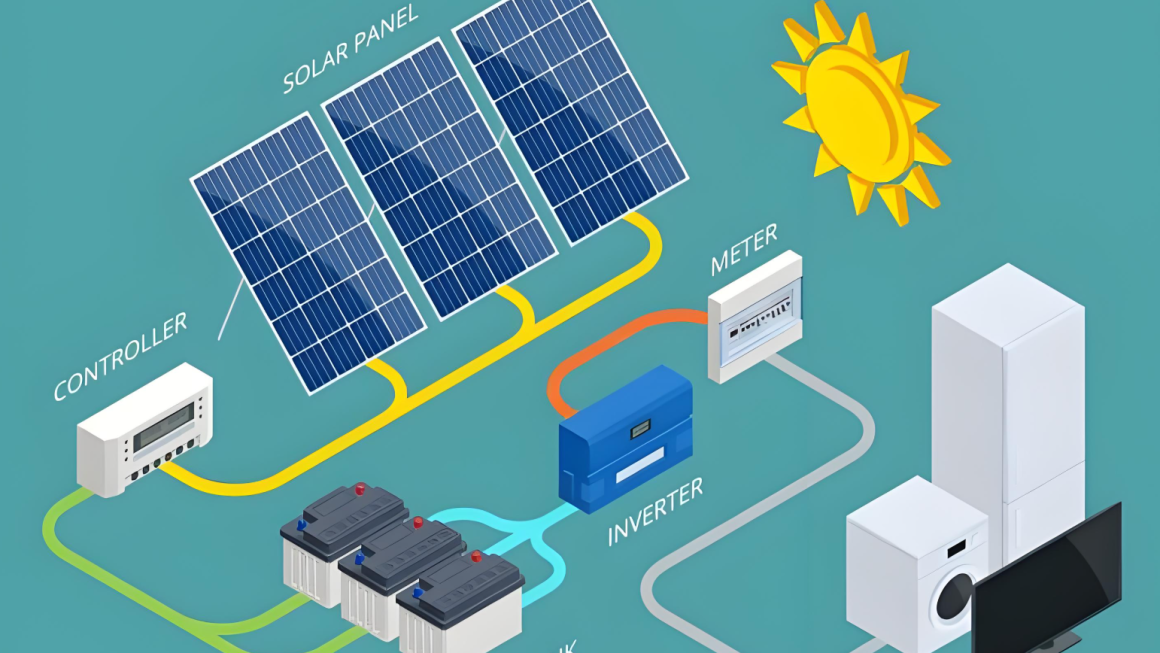
A residential PV + ESS system is a distributed energy setup that combines photovoltaic solar panels with an energy storage system, typically lithium-ion batteries, to provide on-site generation and backup capability. These systems can operate:
- Grid-tied (on-grid): Connected to the public grid, sometimes with net metering or feed-in tariffs.
- Off-grid: Independent of the utility, ideal for remote homes.
- Hybrid: Can switch between grid and off-grid modes, providing maximum flexibility.
Homeowners increasingly prefer hybrid PV + ESS systems for resilience, electricity cost savings, and energy independence.
2. Key Components of a Home PV + Storage System
Every residential PV + storage system includes several core components:
- Solar PV Modules: Generate DC electricity from sunlight.
- Inverter or Hybrid Inverter: Converts DC to AC for household loads and synchronizes with the grid or generator.
- Battery Pack: Stores surplus solar energy for nighttime or outage use.
- Battery Management System (BMS): Ensures safe charging and discharging.
- Energy Management System (EMS): Monitors and optimizes energy flows across sources, loads, and storage.
- Smart Meter / Monitoring Tools: Enables visibility into performance and consumption.
To learn more about inverter pairing, refer to:
👉 How to Match a Battery Pack with a Hybrid Inverter
3. Common Residential PV + Storage Configurations
Let’s explore several practical system configurations:
A. AC-Coupled Systems
In AC-coupled setups, the solar and storage systems each have dedicated inverters. A solar inverter handles the PV modules, while a separate battery inverter controls energy storage.
Typical use case: Homes adding a battery to an existing solar system.
Advantages:
- Modular and flexible.
- Easy retrofit.
- Independent sizing of PV and battery inverters.
Disadvantages:
- More components and cost.
- Slightly lower efficiency due to AC-DC-AC conversions.
B. DC-Coupled Systems
DC-coupled systems share a single hybrid inverter that controls both the solar PV array and the battery pack. Energy flows on the DC side before conversion to AC.
Typical use case: New installations with tight cost and space constraints.
Advantages:
- Higher efficiency (fewer conversions).
- Lower installation cost and simpler wiring.
- Intelligent control of solar + battery via hybrid inverter.
Disadvantages:
- Less flexibility for upgrades.
- Requires careful component compatibility (e.g. voltage matching).
Want more details on choosing the right hybrid inverter?
👉 How to Choose a Hybrid Inverter for Small-Scale PV Projects
C. Off-Grid Systems
These operate completely independently of the grid, relying on solar power and batteries (sometimes with a diesel generator) for 100% of household needs.
Typical use case: Rural homes, cabins, or locations without grid access.
Advantages:
- Full energy independence.
- Self-sufficiency in remote areas.
Disadvantages:
- Higher battery capacity needed.
- Requires robust design to avoid outages.
D. PV + Storage + Grid + EV Charger
The most advanced residential systems now include EV chargers, enabling households to charge electric vehicles with solar energy. These systems often feature advanced EMS integration.
Typical use case: Tech-savvy users or green households with EVs.
Advantages:
- Future-ready configuration.
- More energy self-consumption.
- Higher ROI in areas with time-of-use electricity pricing.
4. Daily Load Curve Considerations
Choosing the right configuration requires an understanding of residential daily load patterns, which typically include:
- Morning peak: 6 AM – 9 AM (appliances, showers, heating).
- Daytime dip: 9 AM – 5 PM (low load, ideal for solar charging).
- Evening peak: 6 PM – 10 PM (cooking, lights, TV, HVAC).
- Nighttime baseline: 11 PM – 5 AM (refrigerators, standby loads).
Batteries must be sized to cover evening peaks, and inverters should be capable of handling peak loads. Learn more:
👉 Typical Daily Load Curve in Residential PV + ESS Systems
5. Factors That Influence System Configuration
Several project-specific variables determine which configuration is ideal:
| Factor | Impact on Design |
|---|---|
| Grid access | Off-grid or grid-connected system |
| Load profile & peak demand | Inverter sizing and battery capacity |
| Solar resource availability | Panel size and layout |
| Roof space or ground area | Determines PV module layout |
| Backup needs (critical load) | Battery backup or generator integration |
| Budget & ROI expectations | Balance between cost, autonomy, and efficiency |
| Local regulations & incentives | Net metering, grid export limits, subsidies |
6. Best Practices for Technical Sourcing
For sourcing professionals, the following tips can help deliver better solutions and win customer trust:
- Match inverter and battery specs (voltage, current, communication protocol).
- Standardize kits for 3kW/5kW/8kW home systems with flexible add-ons.
- Bundle with EMS/monitoring systems to add control and transparency.
- Prioritize certifications (CE, UL, IEC) for international sales.
- Support with system design advice, not just quotations.
To understand how technical value outperforms price-driven sales, see:
👉 Why Technical Knowledge Beats Low Price in ESS Sales
7. Conclusion: Know Your Homeowner
There’s no one-size-fits-all system for residential solar + storage. The right configuration depends on technical constraints, budget, consumption habits, and long-term energy goals. As a technical trading partner, your role is to guide buyers with clarity, accuracy, and speed.
By deeply understanding how each configuration works and offering flexible options—DC-coupled, AC-coupled, or hybrid—you can position your company as a trusted partner, not just a hardware vendor.
Ready to build your residential PV + storage portfolio?
We offer flexible sourcing solutions and system advisory for small-scale solar and battery projects. Get in touch to learn more.