Keywords: lithium battery, LFP vs NMC, energy storage battery chemistry, battery safety
1. Introduction
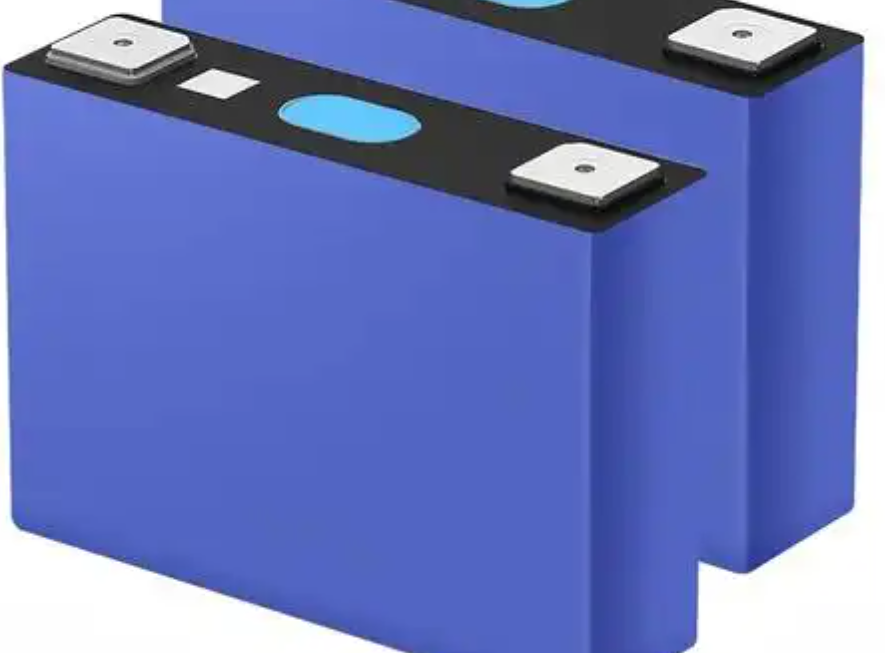
Lithium-ion batteries dominate the energy storage landscape. Two chemistries—LFP and NMC—have emerged as the leaders. Understanding their differences is key to selecting the right battery for your application.
2. Chemistry Basics
- LFP (LiFePO4): Known for safety, thermal stability, and cycle life.
- NMC (LiNiMnCoO2): High energy density, widely used in EVs.
3. Performance Comparison
| Property | LFP | NMC |
| Energy Density | Medium (~150Wh/kg) | High (~220Wh/kg) |
| Safety | Excellent | Good |
| Cycle Life | 4000–6000 | 2000–3000 |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Thermal Stability | High | Medium |
4. Suitability
- LFP: Home and commercial ESS, off-grid
- NMC: Space-limited projects, mobile systems
5. Industry Insight
With CATL and BYD focusing heavily on LFP, global trends are shifting toward LFP for stationary storage due to safety and cost.
6. Conclusion
Choose LFP for stability and cost-efficiency; NMC when space is limited but power demand is high.
👉 We help you source both battery types. Explore your options at gr-newenergy.com.